Wire harnesses, as critical components for electrical and signal transmission, play an indispensable role in automotive, aerospace, industrial automation, and other fields.
Wiring Harness Failure Analysis
Wiring Harness Failure:Terminal Contact Failure
- Causes: Terminal loosening, contamination, corrosion, micro-motion wear.
- Failure Mechanism: Under identical voltage, a smaller effective contact area increases resistance. Current flowing through contact resistance generates abnormal heat, leading to electrolytic oxidation.
- Influencing Factors: Terminal material properties, terminal plating quality, crimping process.
- Typical Manifestations: Abnormal appliance operation (e.g., insufficient light brightness, weak motor rotation), abnormal system voltage drop, localized overheating or even melting of connector plastic. However, short-circuit protection devices may fail to activate.

Wiring Harness Failure:Open Circuit
- Causes of Failure: Mechanical stress, oxidation corrosion, electrochemical corrosion, poor manufacturing processes.
- Failure Mechanism: Stress points in the conductor concentrate at the terminal bend, leading to stress reduction at the structural point and subsequent cracking, ultimately causing terminal fracture.
- Influencing Factors: Incorrect wire selection, improper routing design, inappropriate crimping parameters.
- Typical Manifestation: Electrical appliances may exhibit intermittent operation or complete failure.
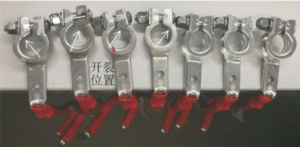
Wiring Harness Failure:Short Circuit
- Causes of Failure: Physical wear, interference between wiring harnesses and other components, vibration friction. Mechanical damage, pinching during assembly.
- Failure Mechanism: Insulation layer damage due to wear or puncture by sharp objects, resulting in contact between two conductors and causing a short circuit.
- Influencing Factors: Material temperature rating, operating environment temperature, duration of operation.
- Typical Manifestations: Fuse blowout, inability to turn off electrical appliances, functional malfunction.
Wiring Harness Failure:Wire Breakage
- Cause: Fatigue fracture of wires due to vibration fatigue or improper installation.
- Failure Mechanism: Improper wire harness design and installation, where repeated bending causes material fatigue leading to wire breakage or overload burnout.
- Influencing Factors: Material fatigue strength, vibration environment, current load.
- Typical Manifestation: Circuit open, infinite resistance (∞Ω).

Wiring Harness Failure:Conductor Corrosion
- Cause: Corrosion occurs when conductors come into contact with corrosive media, reducing the conductor cross-sectional area.
- Failure Mechanism: Prolonged exposure to chemical corrosion from substances like engine oil, acid rain, or solvents diminishes the conductor cross-section. This increases current flow, causing localized overheating and ultimately leading to functional failure.
- Influencing Factors: Environmental humidity, corrosive media, protective measures.
- Typical Manifestations: Deteriorated electrical performance (open circuits), signal attenuation, reduced mechanical properties.
Wiring Harness Failure:Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Failures
- Causes: Shared power supplies are the most common cause of EMC failures, followed by cable routing and enclosure shielding.
- Failure Mechanism: Insufficient spacing between signal lines, inadequate single-layer shielding.
- Influencing Factors: Substandard shielding material properties, design flaws in manufacturing processes.
- Typical Manifestations: Intermittent signal transmission or signal loss.
JinHai’s Solutions
Addressing the above failure modes, JinHai implements solutions across three dimensions: material selection, manufacturing equipment upgrades, and process control:
Material Selection
JinHai employs high-purity copper materials and diverse plating technologies (gold, silver, nickel, tin, etc.) to enhance terminal surface contact wear resistance, oxidation resistance, and material elasticity.
Equipment Enhancement
JinHai employs fully automated wire-cutting and crimping equipment with real-time pressure monitoring to optimize crimping consistency.
Process Control
For applications like smart driving cockpits and airbags, JinHai implements precision twisted-pair wiring during manufacturing to improve harness flexibility.
Conclusion
JinHai delivers systematic solutions starting from fault mode analysis. As technology advances, wiring harness systems face increasingly stringent reliability demands.
Contact us immediately to learn how we can meet your cable and harness requirements. Follow us on Youtube .