This guide will comprehensively explain the entire Wire Harness manufacturing process, covering aspects such as design, assembly materials, production procedures, and quality control.
This guide takes approximately ten minutes to read. We hope the content provides detailed explanations and helps you find useful information.

Component Composition of Wire Harness
A wire harness consists of various functional components and terminals, each of which is indispensable.
- Conductor: The primary connecting wire in a harness, responsible for transmitting electrical power or electronic signals.
- Common materials include copper for its excellent conductivity, with aluminum or tin-plated copper available based on customer requirements.
- Insulation Layer: A protective coating surrounding the conductor, preventing current leakage and short circuits while shielding the conductor from harsh environmental impacts.
- Material selection depends on the harness’s operating environment characteristics and customization needs.
- Connectors: Facilitate plug-and-play connections between harness interfaces and electronic devices or other harnesses.
- Connectors vary in reliability, protection rating, and installation ease, requiring selection based on operating environment and custom specifications.

- Terminal: A critical component for wire connections, consisting of a metal part crimped onto the wire end and installed inside the connector. Primarily made of copper alloys, it can be tin-plated, gold-plated, or silver-plated according to harness manufacturing requirements to enhance conductivity, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance.

- Jacket and Protective Layer: The protective covering of the wire harness, bundling wires with identical functions together to provide comprehensive defense against wear, cuts, and impacts during use. Common types include PVC jackets, corrugated tubing, heat-shrink tubing, and braided sleeves.
- Shielding Layer: A metallic layer protecting the integrity of high-frequency or high-precision harness signals by preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Constructed from metal foil or braided mesh.
- Fastening and Binding Accessories: Utilizes auxiliary materials like adhesive tape, cable ties, and clips to shape, secure, and position the harness within equipment.
- Identification and labeling: Clearly identifies each wire’s function, origin, and destination through color coding, text, or barcodes. Accurate labeling is critical for assembly, debugging, and future maintenance.
- Other components: Customized for specific applications, including integrated elements such as fuses (for overcurrent protection), sealing rings/waterproof plugs (enhancing water and dust resistance), resistors, and sensors.
Manufacturing Process and Equipment for Wire Harness
Precision machinery and stringent quality control are essential capabilities in wire harness manufacturing, while automation levels serve as a key indicator of a manufacturer’s production capacity.
Wire Harness Manufacturing Process Nodes
Digital Drawing Design
During harness drawing design, 3D modeling and 2D drawing generation are performed using software such as EPLAN Harness proD and CATIA. Integration with ERP and MES systems enables end-to-end digital management spanning design, production, and quality traceability.
Wire Processing Stage

- Wire Cutting/Stripping: Precisely cut wire lengths using automated wire cutting and stripping machines, removing insulation from both ends (or multiple sections).
Terminal Crimping and Connection Stage
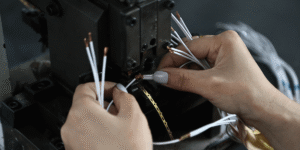
- Terminal Crimping: Cold-press connect wire cores to terminals using specialized crimping equipment. This core process determines electrical performance and mechanical strength, requiring strict control of parameters like crimp height and initial piece quality inspection.
- Welding and Ultrasonic Fusion Equipment: Applications requiring permanent or specialized connections employ welding or ultrasonic fusion technology.
- Connection: Wires with crimped terminals are threaded into pre-drilled holes within the connector housing. Quality issues such as incorrect terminal insertion, reversed orientation, or incomplete seating must be detected.
Assembly and Forming Stage
- Harness Assembly Pinning Board: A workbench for assembling bundled individual wires into complete harnesses at a 1:1 ratio. It guides operators by displaying routing paths, colors, and component information to reduce error rates.
- Final Assembly: Bundled harnesses are secured with tape, corrugated tubing, cable ties, etc., to form the complete wire harness product.
Testing and Quality Inspection Stage

Basic Performance Testing
- Electrical Continuity Testing: Each harness undergoes 100% electrical testing using specialized continuity test benches. This verifies correct circuit connections and detects short circuits, open circuits, or breaks.
- Insulation & Withstand Voltage Testing: Verifies insulation integrity by applying high voltage to detect leakage or insulation breakdown between circuits or to ground.
- Mechanical & Dimensional Inspection: Includes visual checks for damage/contamination, dimensional measurements, physical pull-out force testing of terminals (spot-checked), connector insertion/extraction force testing, color coding verification, and seal installation confirmation.
Harsh Environment Simulation and Tolerance Verification
- Extreme Temperature Conditions: The wiring harness operates normally in extreme environments ranging from -40°C to +85°C.
- Humidity and Heat Aging Conditions: High-temperature, high-humidity environments to evaluate the durability and corrosion resistance of protective coatings.
- Salt Spray Corrosion Conditions: High-salinity corrosive environments to assess the wiring harness’s corrosion resistance.
- Vibration and Shock Conditions: Ensures stable operation of the wiring harness under dynamic conditions involving resonance and impact.
High-efficiency manufacturing equipment forms the foundation for producing high-quality wiring harnesses. With advancements in intelligent production, manufacturing equipment has become increasingly precise and multifunctional.

Wire Harness Manufacturing Equipment
- Automated Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine: Performs wire feeding, cutting, and stripping functions.
- Manual/Automatic Terminal Crimping Machine: Manually or automatically completes multiple processes including wire cutting, dual-end stripping, and dual-end crimping.
Testing Equipment
- Continuity Tester: Essential quality control tool for verifying electrical connectivity of wiring harnesses.
- Pull-off Tester: Used for spot checks or first-article inspection to verify whether the pull-off force of crimped terminals meets standards.
- High-Voltage Tester: Conducts insulation and withstand voltage tests to ensure harness safety under rated voltage.
Summary
In the wire harness manufacturing process, it is essential to understand the operational principles of electrical systems to ensure the efficiency and safety of the harness.
JinHai is a professional wire harness manufacturer with extensive experience, strong technical capabilities, and strict adherence to production standards. Whether it’s forward design from scratch or challenging reverse engineering, we can provide you with a satisfactory solution.
Contact us immediately to learn how we can meet your cable and harness requirements. Follow us on Youtube .