What factors lead to the improper selection of wire harness raw materials?
Standard System for Wire Harness Raw Materials
Wire harnesses are applied across various fields of daily life, each with corresponding industry standards such as IATF 16949, ISO 6722, and IEC 60092. These standards provide performance requirements and testing methods for raw material selection in wire harnesses, serving as a common focus for product design and technical exchange both domestically and internationally.
Conductor Material Selection Criteria and Technical Considerations
- Wires serve as the core for transmitting electrical performance and signals within wiring harnesses. Improper selection of wire gauge and material directly impacts electrical performance and reliability. Copper remains the primary conductor material in the wiring harness industry . Higher copper purity correlates with enhanced harness reliability.
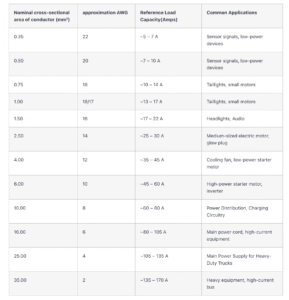
- Conductor cross-sectional area selection requires calculation based on the wire’s current-carrying capacity. The current capacity table provided by SAE J1128 (Figure 2) serves as a reference standard.
- Improper terminal plating treatment will increase the contact resistance of the terminals, thereby affecting the functionality of electrical appliances and potentially creating serious safety hazards. Common plating materials include gold, tin, silver, and nickel. Each type of plating exhibits varying levels of electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance. Precious metals demonstrate the most outstanding performance in both aspects and are consequently the most widely used.
-
Performance Requirements and Selection Criteria for Insulation Materials
Selecting insulation materials requires consideration of multiple factors (such as signal transmission and wire harness flexibility) to ensure electrical safety of the wire harness.
- Material thickness selection must balance wire harness layout and electrical strength, with relevant testing required to validate the rationality of the selection.
- Material flame retardancy is one of the core safety indicators. UL 94 V-0 represents the most common flame retardant rating requirement, and meeting this standard is a mandatory criterion for the wire harness industry.
- The flexibility of insulation materials is selected based on specific application scenarios. The degree of flexibility directly impacts the service life of wire harnesses.
Material Selection and Environmental Adaptability for Connectors
Connectors serve the critical functions of physical protection and environmental sealing, making them an indispensable component in wire harness materials. Common connector materials include PVC, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), chloroprene rubber (CR), and polyurethane (PU), with selection based on specific application requirements.

Different application environments impose distinct requirements on sheath materials.
- High-temperature environments: Select heat-resistant materials such as silicone rubber or specially formulated cross-linked polyolefin.
- Chemically corrosive environments: Choose materials with superior acid and alkali resistance, such as PTFE or specially formulated EPDM rubber.
- Marine environments: Materials must exhibit excellent salt spray resistance and waterproofing properties, with consideration for anti-fungal growth characteristics.
- High-frequency electromagnetic signal environments: Employ composite sheath structures with metal braiding layers to ensure signal integrity while preventing external interference.
- Mechanical protection design for sheaths varies based on specific application scenarios, e.g.:
- Crush-exposed wiring harnesses (e.g., vehicle chassis wiring): Sheaths must possess sufficient compressive strength;
- Outdoor-exposed wiring harnesses: Sheaths require UV resistance;
- Vibration environments (e.g., agricultural machinery): The sheath material should exhibit excellent fatigue resistance and be adapted to the wiring harness’s mounting method.
- Sheath wall thickness must be reasonably designed—moderate thickness provides protection while minimizing costs. Typically, main trunk harness sheaths range from 1.0–2.0 mm thick, while branch harnesses use 0.5–1.0 mm thickness.
JinHai Your Premium Supplier
With 28 years of wire harness manufacturing expertise, JinHai maintains an efficient and rigorous approach to raw material selection. Our design department considers not only standard systems and cost factors but also comprehensively evaluates the performance characteristics and application requirements of conductors, insulation, and sheathing materials. Choosing JinHai means making the optimal choice for your products and costs.
Contact us immediately to learn how we can meet your cable and harness requirements. Follow us on Youtube .